Did you know that the food you eat can directly impact your body’s ability to fight off diseases, slow down aging, and keep your heart healthy? One of the key nutrients responsible for this is vitamin E, a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting your cells from oxidative damage. While most people associate vitamin E with nuts, seeds, and plant oils, beef is also a source of this essential vitamin but how much vitamin E do you actually get from a kilo of beef?
If you’re someone who enjoys a hearty steak or loves to include beef in your diet, understanding the vitamin E content in beef per kilogram can help you make smarter nutritional choices. Whether you’re a health-conscious eater, a fitness enthusiast tracking your micronutrients, or just someone who enjoys a well-balanced diet, knowing the nutritional value of beef: vitamin E levels is essential.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know:
- How much vitamin E is in a kilo of beef?
- Is grass-fed beef richer in vitamin E than grain-fed beef?
- Does cooking affect the vitamin E content in beef?
- Can we enhance beef’s vitamin E levels through diet or supplementation?
Let’s dive deep into the beef vitamin E levels and uncover the facts you never knew about your favorite protein!
Unlocking the Nutritional Value of Beef: Vitamin E Levels Explained
How Much Vitamin E is in a Kilo of Beef?
When we think of beef, we often consider its protein, iron, and B vitamins, but did you know it also contains vitamin E? The amount, however, isn’t as high as in plant based sources like almonds or sunflower seeds. On average, a kilogram (1,000g) of beef contains approximately 1.5–3.5 mg of vitamin E. This amount can vary based on the cut, diet of the cattle, and preparation methods.
To put this into perspective, the recommended daily intake (RDI) for vitamin E is:
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Intake (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | 4 mg |
| Children (1-3 years) | 6 mg |
| Adults (Men & Women) | 15 mg |
| Pregnant Women | 15 mg |
| Breastfeeding Women | 19 mg |
So, if you’re eating a 200g serving of beef, you’re getting about 0.3–0.7 mg of vitamin E, which contributes a small but meaningful portion of your daily needs.
Why Does Vitamin E Matter in Your Diet?
Vitamin E is one of the most powerful antioxidants, which means it helps:
- Protect cells from oxidative stress (reducing risks of chronic diseases)
- Boost immune function and improve your body’s defense system
- Keep your skin glowing by preventing premature aging
- Support heart health by reducing inflammation and maintaining blood vessel function
While beef alone may not provide enough vitamin E to meet daily needs, it plays a supportive role in a balanced diet when paired with vitamin E-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds.
Comparing Vitamin E in Different Meats
Beef isn’t the only meat that contains vitamin E. How does it compare to other popular meats?
For a deeper look into beef’s nutritional benefits, check out this guide on the nutritional value of minced beef.
| Meat Type | Vitamin E Content (mg per kg) |
|---|---|
| Beef | 1.5 – 3.5 mg |
| Chicken | 0.5 – 2 mg |
| Pork | 1 – 2.5 mg |
| Lamb | 1.2 – 3 mg |
| Fish (Salmon) | 3 – 5 mg |
As you can see, salmon and fatty fish contain higher vitamin E levels, while chicken and pork have slightly lower amounts compared to beef. If you rely on meat for vitamin E intake, beef can be a valuable source, especially when combined with a well-rounded diet.
Vitamin E Deficiency: Should You Be Concerned?
Most people who eat a diverse diet don’t have to worry about vitamin E deficiency, but certain groups are more at risk, including:
- People on low-fat diets (since vitamin E is fat-soluble, it needs dietary fat for absorption)
A well-planned diet, such as keto, can help balance healthy fats and vitamin E intake. Check out these keto breakfast ideas for inspiration.
- Those with digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease, which affects nutrient absorption
- Athletes and highly active individuals, who may require higher antioxidant intake
- People who rely too much on processed foods, which are often stripped of essential nutrients
If you fall into one of these categories, it’s even more important to focus on getting enough vitamin E from food sources like beef and pairing it with healthy fats (avocado, nuts, olive oil) to improve absorption.
A Simple Recipe to Boost Your Vitamin E Intake!
Now that you know beef contains vitamin E, why not prepare a delicious, nutrient-rich meal that helps maximize this vitamin?
For another beef-packed meal idea, try this flavorful beef burrito recipe.
Vitamin E-Boosting Beef Stir-Fry with Almonds & Spinach
Ingredients:
- 250g beef (sirloin or ribeye)
- 1 cup baby spinach (rich in vitamin E)
- ¼ cup sliced almonds (high in vitamin E)
- 1 tbsp olive oil (for better vitamin E absorption)
- 1 tsp garlic (adds flavor and antioxidants)
- 1 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tsp sesame oil
- 1 red bell pepper, sliced
Instructions:
- Slice the beef into thin strips. Heat olive oil in a pan and cook the beef on high heat for 2-3 minutes.
- Add garlic and bell pepper, stir-frying for another 2 minutes.
- Toss in the spinach and almonds, stirring until the spinach wilts.
- Drizzle soy sauce and sesame oil over the stir-fry. Mix well and cook for 1 more minute.
- Serve hot and enjoy your vitamin E-packed meal!
Beef may not be the highest source of vitamin E, but it still plays an important role in your diet especially when combined with other nutrient-rich foods. If you’re looking for a balanced way to support your health with vitamin E, incorporating beef alongside vitamin E-rich vegetables, nuts, and healthy fats is a great strategy.
Grass-Fed vs. Grain-Fed Beef: Which Offers More Vitamin E Per Kilogram?
Imagine you’re at the butcher counter, deciding between grass-fed and grain-fed beef. You’ve probably heard that grass-fed beef is healthier but is it actually richer in vitamin E? The answer is a resounding YES! But why? What makes one type of beef more nutritious than the other? Let’s break it down!
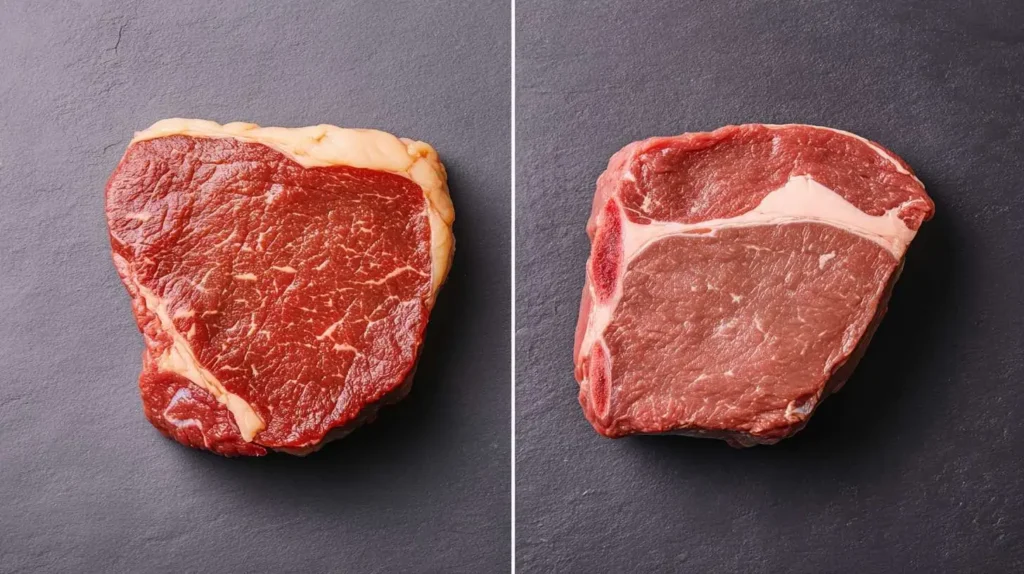
The Key Difference: What Do Cattle Eat?
The main factor that determines the vitamin E content in beef per kilogram is the diet of the cow.
- Grass-fed beef comes from cows that eat a natural diet of grass, forage, and other plants.
- Grain-fed beef comes from cows that eat grains like corn and soy in feedlots, often to fatten them up faster.
Since vitamin E is abundant in fresh grass but lower in grains, cows that graze on grass naturally absorb more vitamin E into their muscles and fat. This means grass-fed beef contains significantly higher levels of vitamin E than grain-fed beef.
Comparing Vitamin E Levels: Grass-Fed vs. Grain-Fed Beef
Multiple studies have confirmed that grass-fed beef can have 2-4 times more vitamin E than grain-fed beef. Check out this comparison:
| Beef Type | Vitamin E Content (mg per kg) |
|---|---|
| Grass-Fed Beef | 4 – 8 mg |
| Grain-Fed Beef | 1.5 – 3.5 mg |
That’s a huge difference! In fact, research shows that grass-fed beef has one of the highest vitamin E levels among red meats, making it a superior choice for anyone trying to increase their vitamin E intake.
Why Is Vitamin E So Much Higher in Grass-Fed Beef?
The reason grass-fed beef is richer in vitamin E comes down to the natural antioxidants found in plants.
- Fresh grass is packed with tocopherols (a form of vitamin E), which the cows absorb when grazing.
- When cows eat grains like corn, they don’t get as much natural vitamin E, resulting in lower amounts in their meat.
- Grass-fed beef also contains more healthy fats (like omega-3s), which help with vitamin E absorption in the body.
In other words, what the cow eats directly affects the nutrition you get when you eat the beef!
Vitamin E Benefits in Beef Consumption: Why It Matters
Now, you might be wondering why should you care about the higher vitamin E levels in grass-fed beef? Well, vitamin E plays an essential role in:
- Strengthening your immune system (especially important for busy professionals & families)
- Preventing inflammation (reducing joint pain, heart disease risks, and even skin aging!)
- Protecting your cells from damage (thanks to its antioxidant properties)
- Keeping your muscles strong (important for athletes and fitness lovers)
For those who prioritize nutrient-dense foods, grass-fed beef is a game-changer. You’re not just getting more vitamin E, but also more omega-3s, less unhealthy fat, and a cleaner source of protein.
Does Vitamin E Supplementation in Cattle Feed Help?
Since grain-fed beef naturally has lower vitamin E levels, some farmers try to boost vitamin E in grain-fed cows by adding supplements to their feed. This can slightly increase the vitamin E content in the meat, but it never reaches the natural levels found in grass-fed beef.
Additionally, beef from vitamin E-supplemented cattle doesn’t have the same health benefits as naturally grass-fed beef because it lacks other vital nutrients found in a natural diet, like omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA).
So, if you want the highest quality beef with the most natural vitamin E benefits, grass-fed is the way to go!
How to Tell If You’re Buying Real Grass-Fed Beef
Not all “grass-fed” labels are created equal! Some products claim to be grass-fed but are grain-finished, meaning the cows ate grass at first but were switched to grain before slaughter. If you want authentic, nutrient-rich grass-fed beef, look for these labels:
- 100% Grass-Fed & Grass-Finished (this means the cow ate only grass its entire life!)
- Certified Organic (organic farms often have strict feeding practices)
- Local Farm-Sourced (small farms usually raise cattle on pasture naturally)
Pro Tip: Grass-fed beef often has a darker red color and yellowish fat due to the higher vitamin E and beta-carotene content. If your beef looks too pale, it’s probably grain-fed!
Easy & Delicious Grass-Fed Beef Recipe: Garlic Butter Steak!
If you want to make the most of your grass-fed beef’s vitamin E levels, here’s a simple yet mouthwatering recipe:
Garlic Butter Grass-Fed Steak
Ingredients:
- 2 grass-fed ribeye steaks (or any cut of choice)
- 2 tbsp butter (helps vitamin E absorption)
- 3 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 tbsp olive oil (another vitamin E booster!)
- 1 tsp sea salt
- ½ tsp black pepper
- 1 tbsp fresh rosemary
Instructions:
- Remove the steaks from the fridge 30 minutes before cooking to let them reach room temperature.
- Heat olive oil in a skillet over medium-high heat.
- Season the steaks with salt and pepper. Sear each side for 3-4 minutes until a golden crust forms.
- Reduce heat to medium, add butter, garlic, and rosemary. Baste the steak with the melted butter for 1-2 minutes.
- Remove from heat, let the steaks rest for 5 minutes, then slice and serve. Enjoy your vitamin E-packed meal!
Which Beef Should You Choose?
So, what’s the verdict? If you want higher vitamin E levels, more antioxidants, and better overall nutrition, grass-fed beef is the superior choice.
- Grass-fed beef has 2-4 times more vitamin E than grain-fed beef
- It’s packed with healthy fats that enhance vitamin E absorption
- It’s more natural, cleaner, and supports better overall health
Choosing grass-fed beef isn’t just about better nutrition it’s about better quality, better taste, and better health benefits for you and your family!
Cooking, Supplements & Diet: Enhancing Beef’s Vitamin E for Maximum Benefits
So, you’ve learned that beef contains vitamin E, and grass-fed beef has significantly more than grain-fed beef. But here’s the next big question: Does cooking destroy vitamin E? And if so, how can you retain and even enhance the vitamin E levels in your meals?
Many people don’t realize that how you cook, store, and prepare beef can greatly impact its nutrient profile especially its vitamin E content. But don’t worry! Today, we’ll uncover the best ways to maximize vitamin E in beef consumption and even explore supplementation strategies that improve the nutritional quality of beef. Let’s get started!
The Impact of Cooking on Beef’s Vitamin E Levels
Did you know that cooking methods can either preserve or deplete vitamin E in beef? Since vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant, it is somewhat heat-sensitive and can break down under extreme temperatures. But not all cooking methods destroy it equally!
If you’re looking for delicious ways to prepare beef while retaining its nutrients, check out these beef round steak recipes.
Here’s how different cooking techniques affect beef vitamin E levels:
| Cooking Method | Impact on Vitamin E Content |
|---|---|
| Grilling (High Heat, Open Flame) | Loses up to 30% of vitamin E due to heat exposure |
| Pan-Frying (Moderate Heat, Butter/Oil) | Loses 10-20% but retains more if cooked with olive oil |
| Slow Cooking (Low Heat, Moist Cooking) | Retains up to 90% of vitamin E |
| Sous Vide (Low Temp, Water Bath) | Preserves nearly 95% of vitamin E |
As you can see, cooking at lower temperatures (like slow cooking and sous vide) helps preserve more vitamin E, while high-heat methods like grilling cause greater losses.
Pro Tip: Cooking beef with vitamin E-rich oils (like olive oil or avocado oil) can help preserve and enhance its vitamin E content!
Best Cooking Tips to Retain Vitamin E in Beef
Want to keep more vitamin E in your beef? Follow these easy cooking tips:
- Use low to moderate heat – Avoid excessive grilling or deep-frying, which break down vitamin E faster.
- Cook with healthy fats – Use olive oil, avocado oil, or butter, which help stabilize vitamin E.
- Don’t overcook your beef – Medium rare to medium doneness preserves more nutrients than well-done.
- Marinate your beef – Studies show that antioxidant-rich marinades (like garlic, rosemary, and lemon) can help protect vitamin E from oxidation during cooking.
- Try slow cooking or sous vide – These gentle cooking methods maximize vitamin E retention and keep beef juicy!
Enhancing Beef’s Vitamin E Through Diet & Supplements
While grass-fed beef naturally contains more vitamin E, there are ways farmers can increase the vitamin E levels in beef even further and it starts with what the cows eat.
Vitamin E Supplementation in Cattle Feed
Farmers sometimes add vitamin E supplements to cattle feed to improve beef quality, shelf life, and nutritional value. This method is especially common in grain-fed cattle, where vitamin E levels are naturally lower.
- How does it work? When cows eat vitamin E-enriched feed, their muscles absorb more vitamin E, which can then be passed on to consumers through beef consumption.
- Does it help? Yes, but not as much as natural grass-feeding. While supplementation can increase beef’s vitamin E levels by 10-20%, it still doesn’t match the higher levels found in grass-fed beef.
Pairing Beef with Vitamin E-Rich Foods for Maximum Absorption
Want to get the most out of your beef’s vitamin E content? Pair it with other vitamin E-rich foods to enhance absorption and boost overall nutrition.
Here’s a quick guide on what to eat with your beef:
| Vitamin E-Rich Food | Best Beef Pairing |
|---|---|
| Avocados | Steak tacos, beef salad |
| Nuts & Seeds | Beef stir-fry with almonds, beef pesto |
| Leafy Greens | Beef & spinach wrap, steak with arugula |
| Olive Oil | Beef marinade, beef & veggie sauté |
Pro Tip: Eating beef with healthy fats (like nuts, avocados, or olive oil) enhances vitamin E absorption, since vitamin E is fat-soluble.
Recipe: Vitamin E-Packed Beef & Avocado Salad
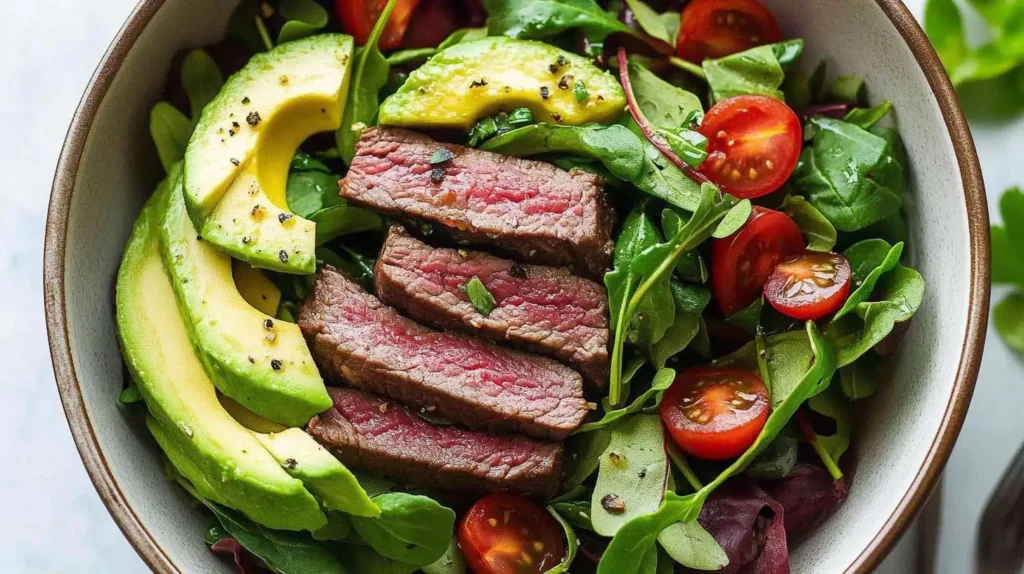

Want a delicious vitamin E-boosting meal that’s quick, easy, and full of nutrients? Try this refreshing Beef & Avocado Salad!
Ingredients:
- 200g grass-fed beef steak, sliced thin
- 1 ripe avocado, diced (rich in vitamin E!)
- 1 cup baby spinach (more vitamin E!)
- ¼ cup toasted almonds (vitamin E powerhouse)
- 1 tbsp olive oil (helps absorb vitamin E)
- 1 tbsp lemon juice
- ½ tsp sea salt & black pepper
- 1 tsp garlic powder
Instructions:
- Heat a pan with olive oil and cook the beef slices until tender.
- In a large bowl, mix spinach, avocado, and almonds.
- Add the cooked beef and toss everything with lemon juice, garlic, salt, and pepper.
- Serve fresh & enjoy a delicious, vitamin E-packed meal!
How to Maximize Vitamin E from Beef
Now you know the best ways to retain and boost vitamin E in beef consumption:
- Choose grass-fed beef for 2-4 times more vitamin E
- Cook beef at lower temperatures (slow cook, sous vide, or pan-sear)
- Use vitamin E-rich oils (olive oil, avocado oil) for cooking
- Pair beef with vitamin E-rich foods (nuts, greens, avocado)
- Look for vitamin E-supplemented beef if grass-fed isn’t available
With the right approach, you can maximize the nutritional benefits of beef and make sure you’re getting the most vitamin E possible in your diet!
Beef & Vitamin E—A Small Nutrient with Big Benefits!
So, how much vitamin E do you really get from a kilo of beef? The answer depends on:
- The type of beef you choose (grass fed vs. grain fed)
- How you cook it
- What you pair it with
While beef isn’t the highest source of vitamin E, it still plays an important role in a balanced diet especially when combined with other nutrient-rich foods. If you want to optimize your vitamin E intake, choosing grass-fed beef, using healthy cooking methods, and pairing it with vitamin E-packed foods will give you the best results!
So, next time you’re at the butcher shop or grocery store, make an informed choice because every bite counts towards a healthier, stronger you!
FAQs About Vitamin E in Beef
What Are the Symptoms of a Lack of Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is essential for protecting your cells from oxidative damage and supporting overall health. A deficiency in vitamin E is rare but can occur in individuals with poor fat absorption or restrictive diets. Symptoms of low vitamin E levels include:
- Muscle weakness – Vitamin E plays a crucial role in nerve function, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness.
- Vision problems – Insufficient vitamin E can cause retinal degeneration, leading to vision issues.
- Weakened immune system – A lack of vitamin E reduces the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Nerve damage & coordination issues – Deficiency can lead to neurological problems, affecting movement and coordination.
- Dry skin & premature aging – Vitamin E is vital for skin health, and low levels may cause dryness and early signs of aging.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to improve your vitamin E intake through a balanced diet that includes vitamin E-rich foods like beef, nuts, and leafy greens.
How Much Vitamin E is in Beef Tallow?
Beef tallow, which is rendered beef fat, contains a small amount of vitamin E, but it’s lower than what is found in beef muscle meat.
- On average, 100g of beef tallow contains approximately 2-4 mg of vitamin E.
- The vitamin E content in tallow depends on whether the beef was grass-fed or grain-fed (grass-fed beef tallow contains more vitamin E).
Since vitamin E is fat-soluble, consuming beef tallow with other vitamin E-rich foods (like avocado, spinach, or nuts) can enhance absorption and overall health benefits.
How Do You Measure Vitamin E in Food?
Vitamin E in food is measured in milligrams (mg) or International Units (IU). The most common way to determine vitamin E levels is through scientific laboratory testing, but if you’re looking for an estimate, you can:
- Check nutrition labels – Many packaged foods list their vitamin E content per serving.
- Use online food databases – Websites like USDA FoodData Central provide vitamin E values for different foods.
- Understand common food sources – Nuts, seeds, fish, and grass-fed beef naturally contain higher levels of vitamin E.
For more precise measurements, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used in food labs to analyze tocopherol levels (the scientific term for vitamin E compounds).
Which Meat Has the Most Vitamin E?
If you’re looking for meat sources high in vitamin E, here’s a comparison of vitamin E levels in different meats per kilogram:
| Meat Type | Vitamin E Content (mg per kg) |
|---|---|
| Grass-Fed Beef | 4 – 8 mg |
| Grain-Fed Beef | 1.5 – 3.5 mg |
| Chicken (Dark Meat) | 0.5 – 2 mg |
| Lamb | 1.2 – 3 mg |
| Pork (Lean Cuts) | 1 – 2.5 mg |
| Salmon & Fatty Fish | 3 – 5 mg |
- Grass-fed beef has one of the highest vitamin E levels among red meats.
- Fatty fish like salmon is also a great source of vitamin E and healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Chicken contain less vitamin E, but the levels depend on the animal’s diet.
If you’re aiming to increase your vitamin E intake from meat, grass-fed beef and fatty fish are your best options!
Conclusion:
So, how much vitamin E do you really get from a kilo of beef? The answer depends on the type of beef you choose, how you cook it, and what you pair it with. Grass-fed beef contains 2-4 times more vitamin E than grain-fed beef, making it a superior choice for those looking to boost their antioxidant intake. But that’s not all your cooking methods and pairing beef with vitamin E-rich foods can further enhance its benefits.
To get the most vitamin E from your beef, opt for low-heat cooking techniques, use healthy fats like olive oil, and combine your beef with nutrient-packed foods like avocados, nuts, and leafy greens. And if grass-fed beef isn’t an option, consider vitamin E-supplemented beef for a healthier alternative.
At the end of the day, beef can be a valuable part of a balanced diet not just for its protein and iron, but also for its vitamin E content. So, next time you fire up the grill or cook up a steak, remember: every choice you make impacts your health!

